
Of course, frequent blood glucose monitoring by bedside capillary testing is needed to minimise the likelihood of hypoglycaemia. Hyperinsulinaemia/euglycaemia therapy (HIET) consists of the infusion of high-dose regular insulin (most commonly 0.5 to 1 IU/kg per hour). Although the mechanism of action is less well understood in this condition, some experimental data suggesting a potential benefit of HIET in β-adrenergic blocker toxicity are discussed clinical data are currently lacking. While we await further well-designed clinical trials, some rational recommendations are made about the use of HIET in severe CBB overdose.

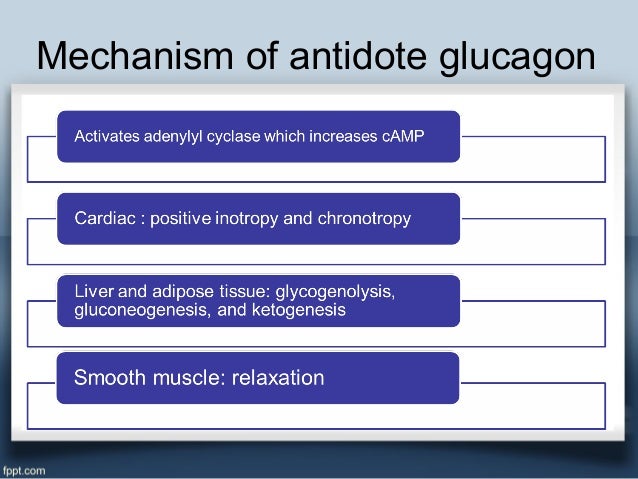
#Glucagon as beta blocker antidote series
Clinical experience currently consists only of a few isolated cases or short series in which the administration of HIET substantially improved cardiovascular conditions in life-threatening CCB poisonings, allowing the progressive discontinuation of vasoactive agents. Studies in experimental verapamil poisoning in dogs have shown that HIET significantly improves metabolism, haemodynamics and survival in comparison with conventional therapies. Insulin administration seems to allow the switch of the cell metabolism from fatty acids to carbohydrates that is required in stress conditions, especially in the myocardium and vascular smooth muscle, resulting in an improvement in cardiac contractility and restored peripheral resistances. This paper reviews the patho-physiological principles underlying HIET. Indeed, experimental data and clinical experience, although limited, suggest that it could be superior to conventional pharmacological treatments including calcium salts, adrenaline (epinephrine) or glucagon. HIET has been proposed as an adjunctive approach in the management of overdose of calcium-channel blockers (CCBs). Hyperinsulinaemia/euglycaemia therapy (HIET) consists of the infusion of high-dose regular insulin (usually 0.5 to 1 IU/kg per hour) combined with glucose to maintain euglycaemia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
